Introduction
Soil degradation due to nutrient loss is a major challenge in modern agriculture. Continuous cropping without replenishing nutrients reduces soil fertility, lowers yields, and increases dependence on chemical fertilizers. This depletion also harms soil structure, microbial activity, and organic matter, making farming less sustainable. A key solution is integrating cover crops between main cropping seasons. These cover crops restore nutrients, improve soil health, and reduce reliance on synthetic inputs. By adopting cover crops, farmers can enhance fertility, prevent erosion, and promote sustainable agriculture. Below, we outline the top five crops to grow between seasons for better soil health and fertility.

1. Clover
Clover is a nitrogen-fixing legume that significantly enhances soil quality. It helps suppress weeds, prevent soil erosion, and improve soil structure. Its deep root system promotes aeration and increases water retention, making the soil more resilient for future crops. Research shows that incorporating clover into crop rotation can raise soil nitrogen levels by up to 100 kg/ha per year (FAO, 2021).
2. Sunhemp
Sunhemp is well-known for its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen and enhance soil organic matter. This fast-growing legume also helps suppress weeds and reduce soil compaction. Research indicates that sunhemp can contribute approximately 120-140 kg/ha of nitrogen to the soil within 8 to 12 weeks of growth (ICAR, 2020). Its deep-rooted system improves soil aeration and increases water infiltration, making it an ideal choice for sustainable farming.
3. Mustard
Mustard is an excellent choice for a cover crop because of its bio-fumigation properties. It releases compounds that help control soil-borne pests and pathogens, thereby reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Additionally, mustard grows quickly, producing a significant amount of biomass that increases soil organic content and improves soil structure. Research indicates that mustard cover crops can reduce nematode populations by 30-40% (USDA, 2019), making them a valuable option for farmers.
4. Buckwheat
Buckwheat is a fast-growing crop recognized for its ability to scavenge phosphorus from the soil, which makes this nutrient available for future crops. Additionally, buckwheat enhances soil aggregation and inhibits weed growth, thereby minimizing competition for main crops. Studies indicate that buckwheat can increase phosphorus availability by up to 25% (FAO, 2021), resulting in improved nutrient uptake for subsequent crops.
5. Cowpea
Cowpea is a versatile legume that not only fixes atmospheric nitrogen but also improves soil texture and moisture retention. It produces a high biomass yield, which enhances soil organic matter and supports microbial activity. Research has shown that cowpeas can contribute approximately 60-100 kg of nitrogen per hectare to the soil (ICRISAT, 2020). This contribution helps reduce dependence on synthetic fertilizers and improves overall soil fertility.
Benefits of Using Cover Crops
- Prevents Soil Erosion: The extensive root systems of cover crops bind soil particles together, reducing topsoil loss caused by wind and water erosion. This helps maintain soil depth and structure, ensuring long-term agricultural productivity.
- Enhances Soil Fertility: Nitrogen-fixing legumes improve soil nutrient content, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. By naturally replenishing nitrogen, these crops promote healthier plant growth and reduce fertilizer costs for farmers.
- Improves Soil Structure: Cover crops increase soil organic matter, improving aeration and water retention. This leads to better root development in future crops and enhances overall soil resilience.
- Weed Suppression: Fast-growing cover crops outcompete weeds, reducing weed pressure and herbicide reliance. This natural weed control method minimizes labour and chemical input while fostering a healthier growing environment.
- Pest and Disease Management: Some cover crops, like mustard, produce natural biofumigants that control soil-borne pests and pathogens. These biofumigants help reduce the risk of plant diseases, leading to stronger and more resilient crops.
- Moisture Conservation: Cover crops reduce evaporation and enhance water infiltration, ensuring better moisture availability for subsequent crops. This improves drought resistance and maintains soil hydration for optimal plant growth.
What Research says
Research has consistently demonstrated that incorporating cover crops into agricultural systems yields significant improvements in soil health. Key findings from various studies include:
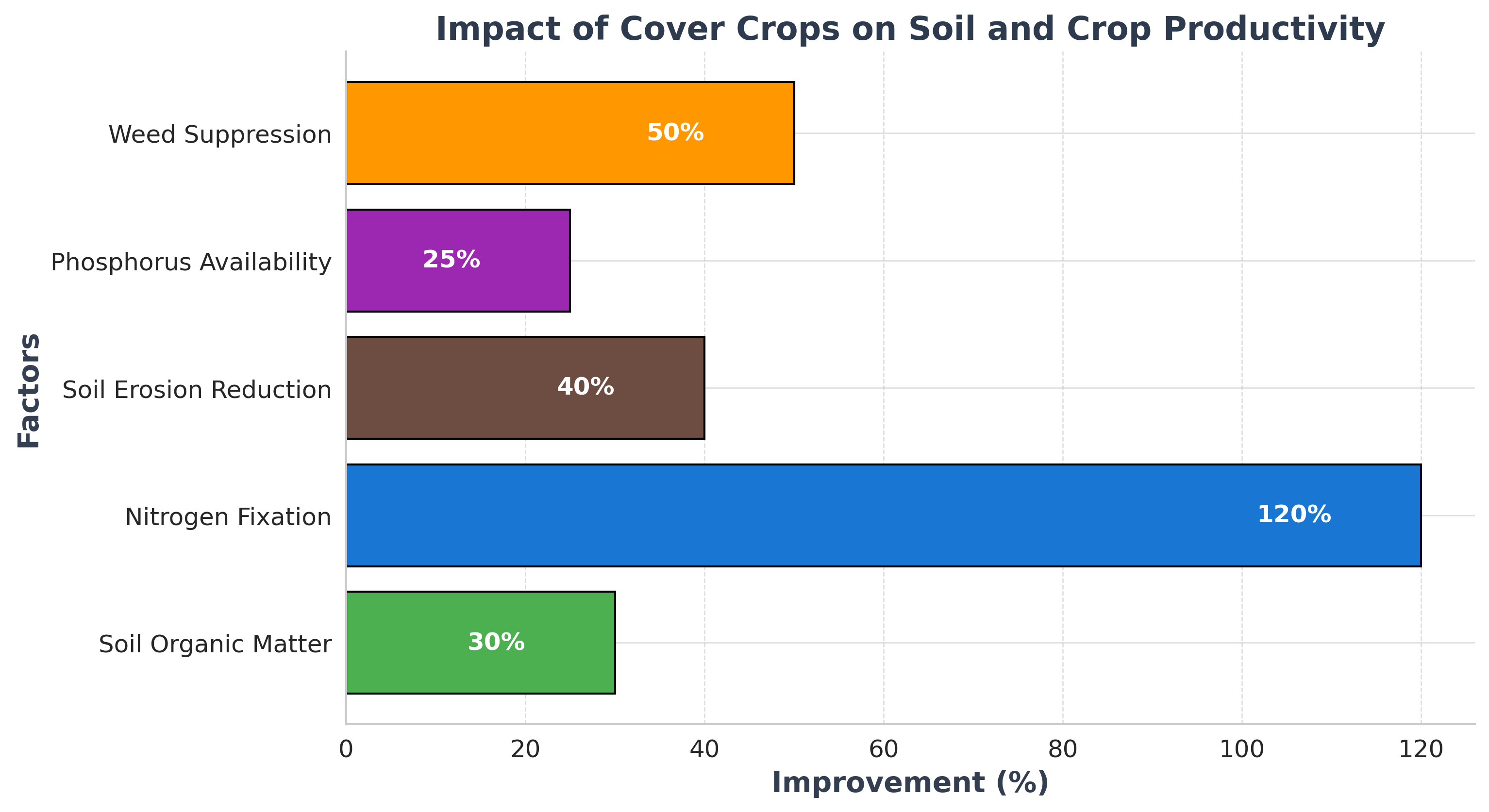
(The bar graph illustrates the positive impact of cover crops on soil health and crop productivity.)
Conclusion:
Sustainable farming practices require decisive soil management strategies, and cover cropping is a critical technique that enhances soil fertility, reduces erosion, and improves soil structure. The five crops—clover, sunn hemp, mustard, buckwheat, and cowpea—are highly effective in replenishing nutrients, suppressing pests, and boosting overall soil health. These crops play an indispensable role in preventing soil erosion, protecting farmlands from degradation, and enhancing water retention capacity. By integrating these cover crops into your farming cycle, you will not only achieve long-term sustainability and productivity but also dramatically reduce input costs. Whether you are a small-scale farmer or overseeing extensive fields, adopting these cover crops will significantly elevate your efforts in soil conservation and agricultural sustainability.
Source and reference:
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO, 2021) – Studies on soil improvement through cover crops, nitrogen fixation, and phosphorus availability.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR, 2020) – Research on Sunn Hemp’s nitrogen contribution and its benefits for soil health.
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA, 2019) – Findings on mustard cover crops and their effectiveness in reducing nematode populations
- Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (SARE)– Reports on the role of cover crops in erosion control, soil organic matter enhancement, and overall soil structure improvement.
- International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT, 2020) – Research on cowpea’s nitrogen-fixing ability and soil improvement.



